Overview
Action Timeout allows you to set a timeout period for actions on a device if they remain stuck in any state other than “Completed” or “Failed.”Why Use Action Timeouts?
In certain situations, an action may get stuck in a particular state, preventing subsequent actions from executing. By setting an action timeout, you can mark these stuck actions as “Failed” to free up the device for future tasks.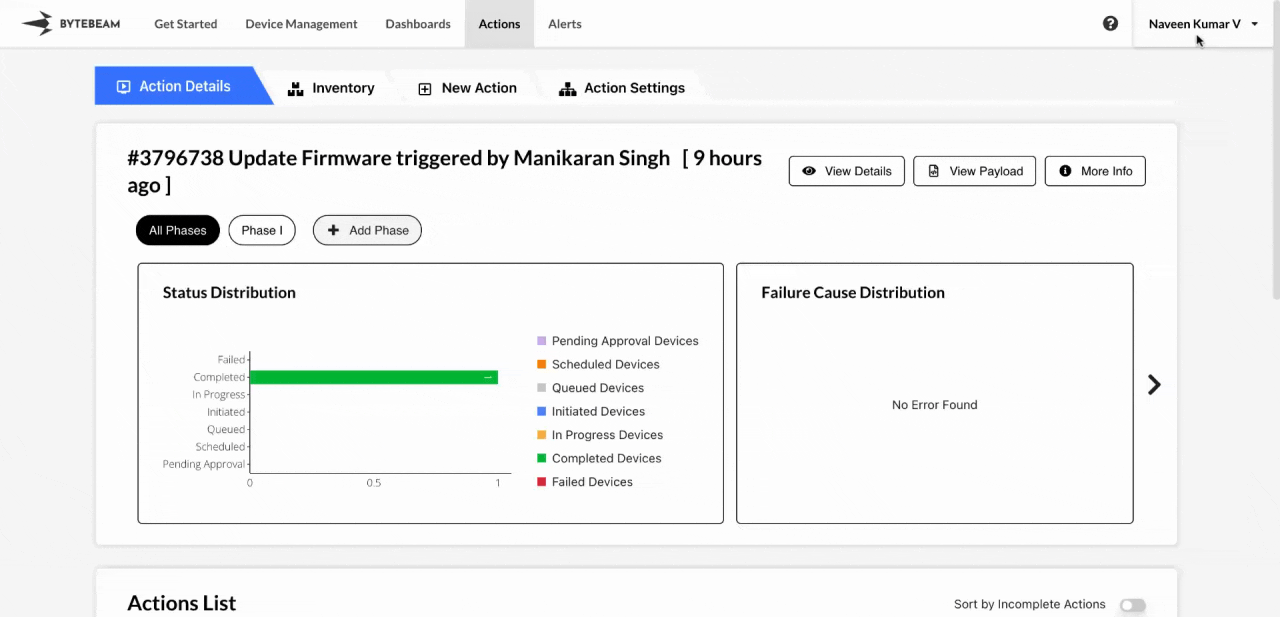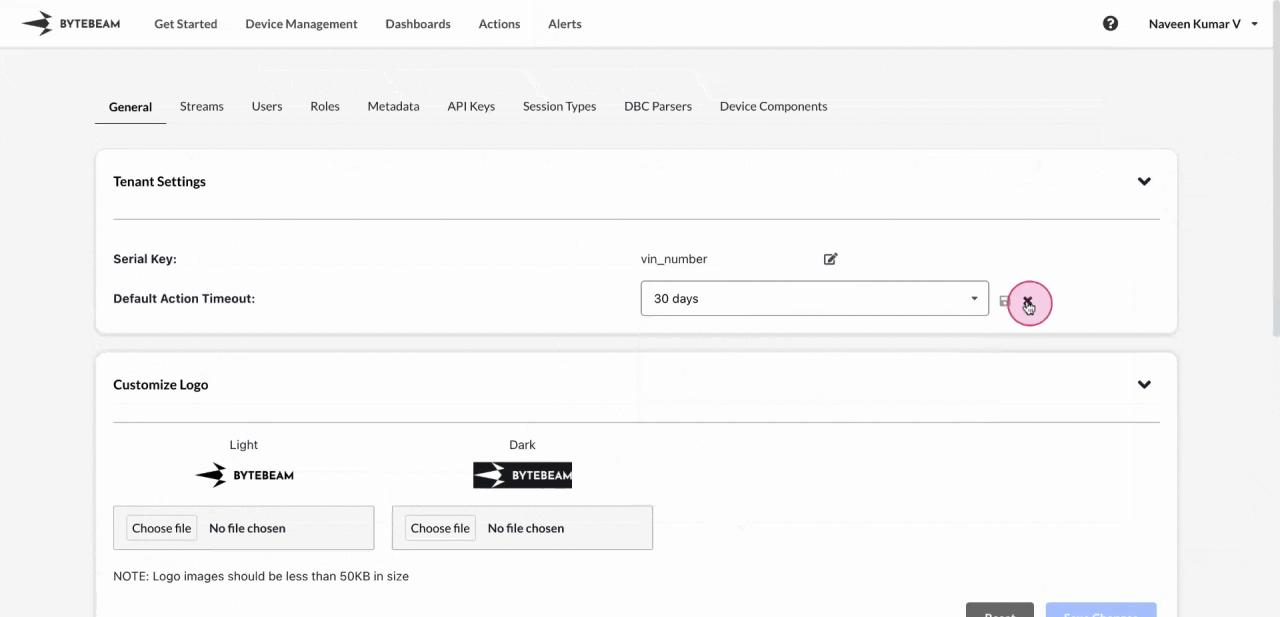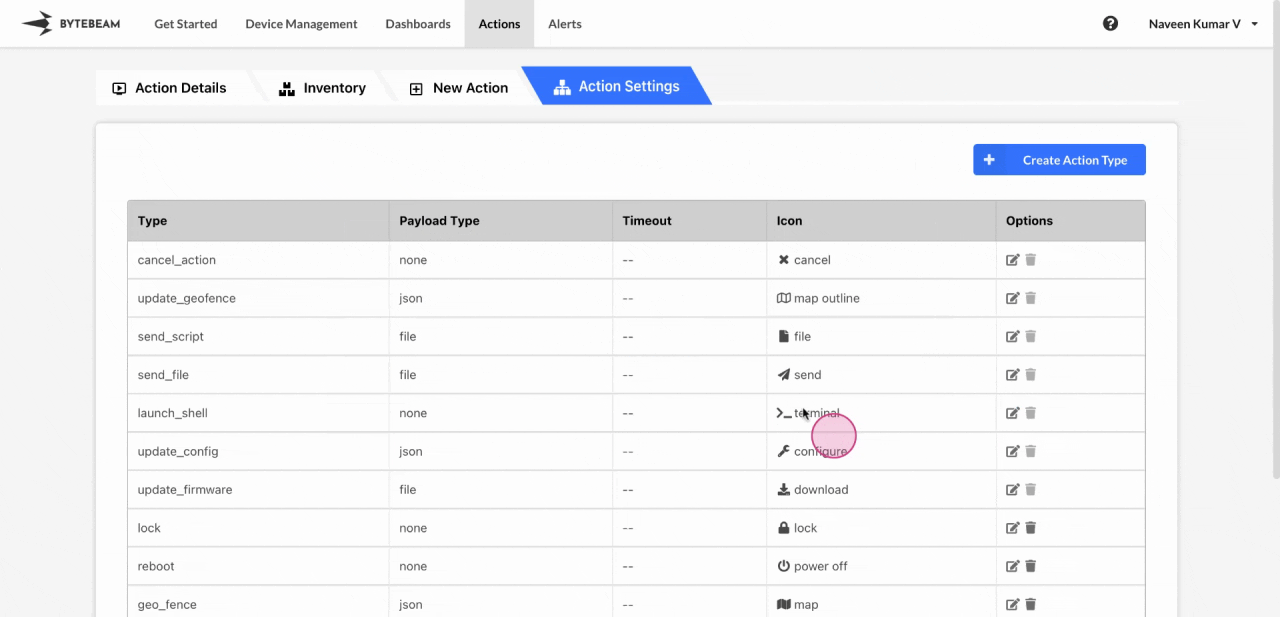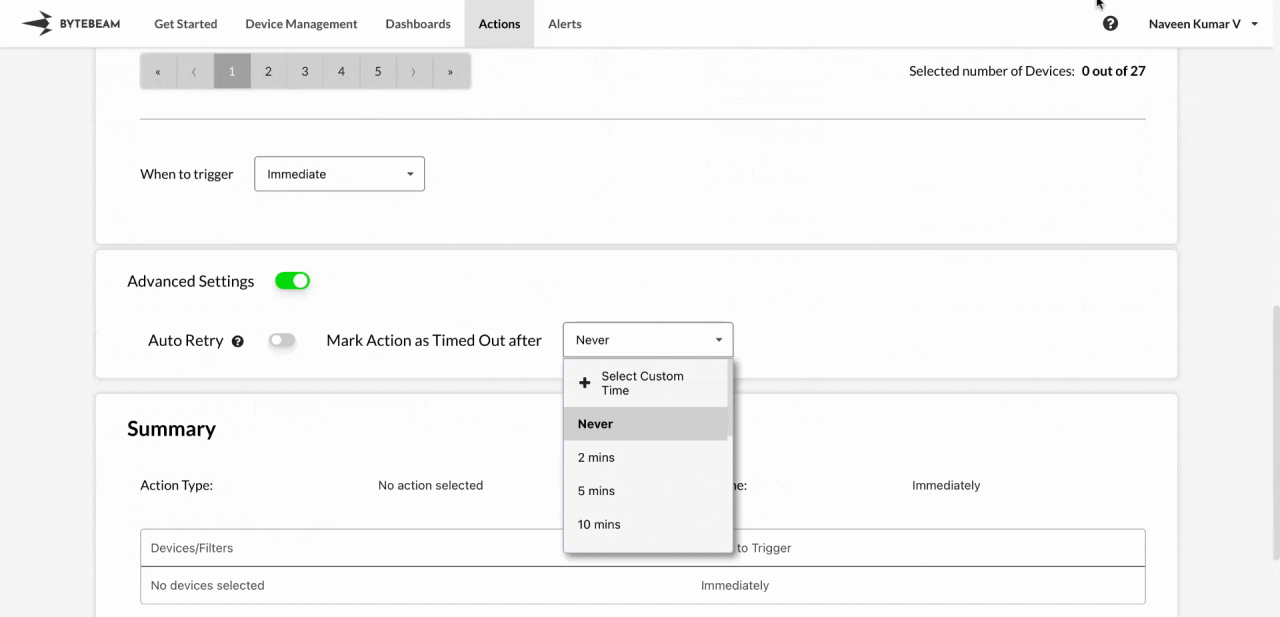
Timeout Configuration Options
Timeouts can be configured in three places: Action Types - Specific to individual action types. Global Settings - Applies to all action types. Advanced Settings - Global for all action types but only affects actions in the “Scheduled” state.Action Types Timeout
Set timeouts for individual action types, applicable if they’re stuck in any state other than “Scheduled,” “Failed,” or “Completed.” To set a timeout for an action type:Go to Action Types and Edit
Go to Action Types and click on the edit icon next to the action type you want to update.
Global Timeout
The global timeout applies to all action types that are stuck in any state other than “Scheduled,” “Failed,” or “Completed.”The default global timeout for new projects is set to 30 days.
Edit Global Timeout
Go to the General tab, and click the edit icon next to Default Action Timeout.
Advanced Settings Timeout
This timeout applies globally to all action types but only affects actions that are stuck in the “Scheduled” state. Use Case: If you have a phased action with a success-rate dependency, and a prior phase does not meet its criteria, the next phase may get stuck in “Scheduled.” This timeout will help mark those phases as “Failed” to allow progression.The default for scheduled actions is set to “Never”.
Summary of Timeout Precedence
For actions stuck in any state other than “Scheduled,” “Completed,” or “Failed,” the timeout is checked in this order:- Action Types Timeout (if configured)
- Global Timeout (if action types timeout is not configured)